Priority scheduling
- In priority scheduling , a priority is associated with all processes.
- Process are executed in sequence according to their priority.
- The CPU time is allocated to the process with highest
priority.
- If the priority of two or more processes are equal than the
process that has been inserted first
into the ready queue is selected
for execution. In other words, FCFS scheduling is performed when wo or more
processes have same priority.
- The priorities are implemented as affixed range of numbers
such as 0to 7 or 0 to 4,095.
- In other system, a low number indicates a high priority . in
that case,a process with priority 0 is executed first.
- Priorities can be defined in two ways : internal or
externall.
- Priority scheduling can be preemptive or non preemptive.
- In preemptive
priority scheduling, scheduler allocates the CPU to the new process if the priority
of new process is higher than priorityof the running process.
- In non-preemptive
priority scheduling, the running process is not interrupted even if new process
has a higher priority. In this case the new process will be placed at the head
of ready queue.
Characteristics of Priority Scheduling
- A CPU algorithm that schedules processes based on priority.
- It used in Operating systems for performing batch processes.
- If two jobs having the same priority are READY, it works on a FIRST COME, FIRST SERVED basis.
- In priority scheduling, a number is assigned to each process that indicates its priority level.
- Lower the number, higher is the priority.
- In this type of scheduling algorithm, if a newer process arrives, that is having a higher priority than the currently running process, then the currently running process is preempted.
Example of Priority Scheduling
Consider following five processes P1 to P5. Each process has its unique priority, burst time, and arrival time.
| Process | Priority | Burst time | Arrival time |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| P2 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| P3 | 1 | 7 | 6 |
| P4 | 3 | 4 | 11 |
| P5 | 2 | 2 | 12 |
Step 0) At time=0, Process P1 and P2 arrive. P1 has higher priority than P2. The execution begins with process P1, which has burst time 4.
Step 1) At time=1, no new process arrive. Execution continues with P1.
Step 2) At time 2, no new process arrives, so you can continue with P1. P2 is in the waiting queue.
Step 3) At time 3, no new process arrives so you can continue with P1. P2 process still in the waiting queue.
Step 4) At time 4, P1 has finished its execution. P2 starts execution.
Step 5) At time= 5, no new process arrives, so we continue with P2.
Step 6) At time=6, P3 arrives. P3 is at higher priority (1) compared to P2 having priority (2). P2 is preempted, and P3 begins its execution.
| Process | Priority | Burst time | Arrival time |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| P2 | 2 | 1 out of 3 pending | 0 |
| P3 | 1 | 7 | 6 |
| P4 | 3 | 4 | 11 |
| P5 | 2 | 2 | 12 |
Step 7) At time 7, no-new process arrives, so we continue with P3. P2 is in the waiting queue.
Step 8) At time= 8, no new process arrives, so we can continue with P3.
Step 9) At time= 9, no new process comes so we can continue with P3.
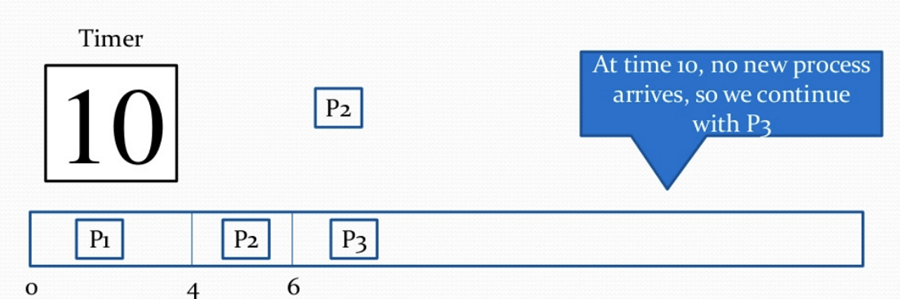
Step 10) At time interval 10, no new process comes, so we continue with P3
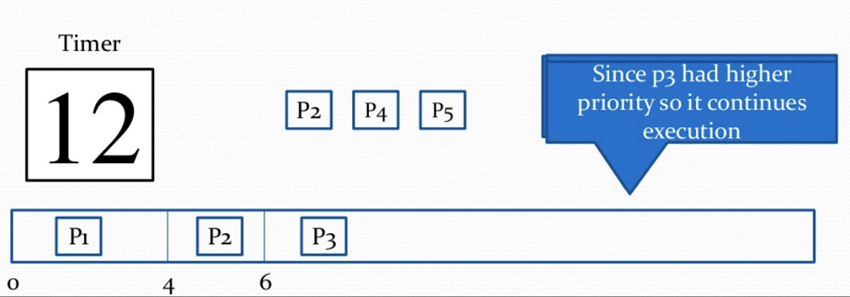
Step 11) At time=11, P4 arrives with priority 4. P3 has higher priority, so it continues its execution.
| Process | Priority | Burst time | Arrival time |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| P2 | 2 | 1 out of 3 pending | 0 |
| P3 | 1 | 2 out of 7 pending | 6 |
| P4 | 3 | 4 | 11 |
| P5 | 2 | 2 | 12 |
Step 12) At time=12, P5 arrives. P3 has higher priority, so it continues execution.
Step 13) At time=13, P3 completes execution. We have P2,P4,P5 in ready queue. P2 and P5 have equal priority. Arrival time of P2 is before P5. So P2 starts execution.
| Process | Priority | Burst time | Arrival time |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| P2 | 2 | 1 out of 3 pending | 0 |
| P3 | 1 | 7 | 6 |
| P4 | 3 | 4 | 11 |
| P5 | 2 | 2 | 12 |
Step 14) At time =14, the P2 process has finished its execution. P4 and P5 are in the waiting state. P5 has the highest priority and starts execution.
Step 15) At time =15, P5 continues execution.
Step 16) At time= 16, P5 is finished with its execution. P4 is the only process left. It starts execution.
Step 17) At time =20, P5 has completed execution and no process is left.
Step 18) Let's calculate the average waiting time for the above example.
Waiting Time = start time - arrival time + wait time for next burst
P1 = o - o = o P2 =4 - o + 7 =11 P3= 6-6=0 P4= 16-11=5 Average Waiting time = (0+11+0+5+2)/5 = 18/5= 3.6
Advantages of priority scheduling
Here, are benefits/pros of using priority scheduling method:
- Easy to use scheduling method
- Processes are executed on the basis of priority so high priority does not need to wait for long which saves time
- This method provides a good mechanism where the relative important of each process may be precisely defined.
- Suitable for applications with fluctuating time and resource requirements.
Disadvantages of priority scheduling
Here, are cons/drawbacks of priority scheduling
- If the system eventually crashes, all low priority processes get lost.
- If high priority processes take lots of CPU time, then the lower priority processes may starve and will be postponed for an indefinite time.
- This scheduling algorithm may leave some low priority processes waiting indefinitely.
- A process will be blocked when it is ready to run but has to wait for the CPU because some other process is running currently.
- If a new higher priority process keeps on coming in the ready queue, then the process which is in the waiting state may need to wait for a long duration of time.
Summary:
- Priority scheduling is a method of scheduling processes that is based on priority. In this algorithm, the scheduler selects the tasks to work as per the priority.
- In Priority Preemptive Scheduling, the tasks are mostly assigned with their priorities.
- In Priority Non-preemptive scheduling method, the CPU has been allocated to a specific process.
- Processes are executed on the basis of priority so high priority does not need to wait for long which saves time
- If high priority processes take lots of CPU time, then the lower priority processes may starve and will be postponed for an indefinite time.
















Comments
Post a Comment