Multi Level
Queue Scheduling (MLQ)
·
Multilevel queue scheduling classifies the processes
according to their types for example, a multilevel queue scheduling algorithm
makes a common.
·
In this scheduling ready queue is divided into various queue
that are called sub queues. A subqueue is a distinct operational queue
·
The process are permanently assigned to subqueues, generally
based on some property of the process such as memory size,priority or process
type
·
Each subqueue has its process sucheduling algorithm. For
example interactive process at the foreground may use round robin scheduling
while batch jobs at the background may use the FCFS method
·
For example, consider a system with four different queues
1. System processes
2. Interactive processes
3. End-user processes
4. Interactive processes
·
In this example, each queue has absolute priority absolute
over low priority queues. No process in a batch queue could run unless the
queue for system process and interactive processes were all empty.
·
If an interactive process entered the ready queue
while a batch process was running the batch process would be preempted. For
example,solaries 2 operating system uses this form of algorithm
Example Problem :
Consider below table of four processes under Multilevel queue scheduling.Queue number denotes the queue of the process.
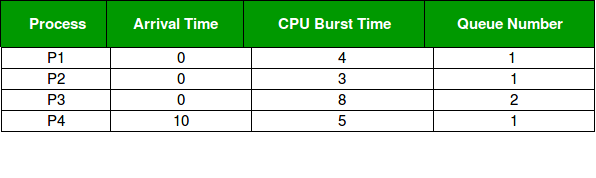
Priority of queue 1 is greater than queue 2. queue 1 uses Round Robin (Time Quantum = 2) and queue 2 uses FCFS.
Below is the gantt chart of the problem :
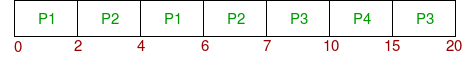
At starting both queues have process so process in queue 1 (P1, P2) runs first (because of higher priority) in the round robin fashion and completes after 7 units then process in queue 2 (P3) starts running (as there is no process in queue 1) but while it is running P4 comes in queue 1 and interrupts P3 and start running for 5 second and after its completion P3 takes the CPU and completes its execution.
Advantages:
- The processes are permanently assigned to the queue, so it has advantage of low scheduling overhead.
Disadvantages:
- Some processes may starve for CPU if some higher priority queues are never becoming empty.
- It is inflexible in nature.
Comments
Post a Comment