Micro kernel architecture
What is Kernel?
A kernel is an important part of an OS that manages system resources. It also acts as a bridge between the software and hardware of the computer. It is one of the first program which is loaded on start-up after the bootloader. The Kernel is also responsible for offering secure access to the machine's hardware for various programs. It also decides when and how long a certain application uses specific hardware.
What is Microkernel?
Microkernel is a software or code which contains the required minimum amount of functions, data, and features to implement an operating system. It provides a minimal number of mechanisms, which is good enough to run the most basic functions of an operating system. It allows other parts of the operating system to be implemented as it does not impose a lot of policies.
Microkernels and their user environments are usually implemented in the C++ or C programming languages with a little bit of assembly. However, other implementation languages are possible with some high-level coding.
What is a Monolithic Kernel?
Monolithic Kernel runs all the basic system services like process management, Memory management, I/O communication, and interrupt handling, file system, etc in kernel space.
In this type of Kernel approach, the entire operating system runs as a single program in kernel mode. The operating system is written as a collection of procedures that are linked together into a large executable binary program.
3. Virtual machine architecture
Microkernel Architecture
A Microkernel is the most important part for correct implementation of an operating system. You can see in the below-given diagram, that Microkernel fulfills basic operations like memory, process scheduling mechanisms, and inter-process communication.
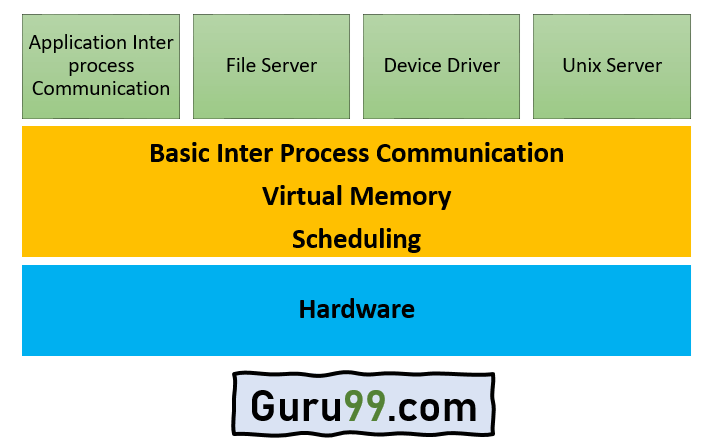
Microkernel is the only software executing at the privileged level. The other important functionalities of the OS are removed from the kernel-mode and run in the user mode. These functionalities may be device drivers, application, file servers, interprocess communication, etc.
Components of Microkernel
A microkernel comprises only the core functionalities of the system. A component is included in the Microkernel only if putting it outside would interrupt the functionality of the system. All other non-essential components should be put in the user mode.
The minimum functionalities required in the Microkernel are:
- Memory management mechanisms like address spaces should be included in the Microkernel. It also contains memory protection features.
- Processor scheduling mechanisms should contain process and thread schedulers.
- Inter-process communication manages the servers that run their own address spaces.
Difference Between Microkernel and Monolithic Kernel
| Parameters | Monolithic kernel | MicroKernel |
| Basic | It is a large process running in a single address space | It can be broken down into separate processes called servers. |
| Code | In order to write a monolithic kernel, less code is required. | In order to write a microkernel, more code is required |
| Security | If a service crashes, the whole system collapses in a monolithic kernel. | If a service crashes, it never affects the working of a microkernel. |
| Communication | It is a single static binary file | Servers communicate through IPC. |
| Example | Linux, BSDs, Microsoft Windows (95,98, Me), Solaris, OS-9, AIX, DOS, XTS-400, etc. | L4Linux, QNX, SymbianK42, Mac OS X, Integrity, etc. |
Advantages of Microkernel
Here, are the pros/benefits of using Microkernel
- Microkernel architecture is small and isolated therefore it can function better.
- Microkernels are secure because only those components are included that disrupt the functionality of the system otherwise.
- The expansion of the system is more accessible, so it can be added to the system application without disturbing the Kernel.
- Microkernels are modular, and the different modules can be replaced, reloaded, modified without even touching the Kernel.
- Fewer system crashes when compared with monolithic systems.
- Microkernel interface helps you to enforce a more modular system structure.
- Without recompiling, add new features
- Server malfunction is also isolated as any other user program's malfunction.
- Microkernel system is flexible, so different strategies and APIs, implemented by different servers, which can coexist in the system.
- Increased security and stability will result in a decreased amount of code which runs on kernel mode
Disadvantage of Microkernel
Here, are drawback/cons of using Microkernel:
- Providing services in a microkernel system are expensive compared to the normal monolithic system.
- Context switch or a function call needed when the drivers are implemented as procedures or processes, respectively.
- The performance of a microkernel system can be indifferent and may lead to some problems.
Summary:
- A kernel is an important part of an OS that manages system resources.
- A microkernel is a software or code which contains the required minimum amount of functions, data, and features to implement an operating system.
- In Monolithic Kernel approach, the entire operating system runs as a single program in kernel mode
- A Microkernel is the most important part for correct implementation of an operating system.
- A microkernel comprises only the core functionalities of the system.
- A monolithic kernel is a large process running in a single address space, whereas Microkernel can be broken down into separate processes called servers.
- Microkernel architecture is small and isolated therefore it can function better
- Providing services in a microkernel system are expensive compared to the normal monolithic system.
Comments
Post a Comment