Exokernel architecture
Most of us know what kernels are and how do they work to make programmers’ lives easier. But, how many of us know what exokernels are? I hope you will be able to get a brief introduction on this terminology through this blog.
Let’s start with a brief introduction on kernel.
What is a kernel?
A kernel is the foundational layer of an operating system that functions at a basic level, communicating with hardware and managing resources, such as CPU and the memory. It works as an interface between the user application and the hardware.


There are two main types of kernel
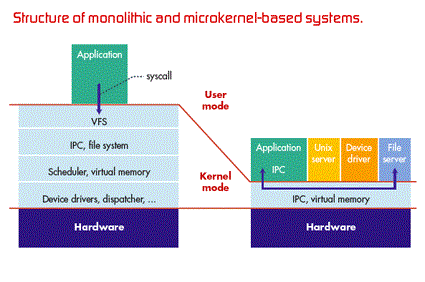
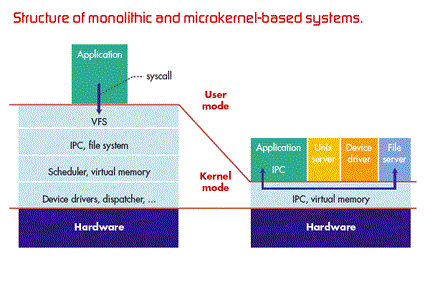
1. Micro kernel
2. Monolithic Kernel
3. Virtual machine architecture
Now let’s head into our main focus.
What is an Exokernel?
Exokernel is an operating system developed at the MIT that provides application-level management of hardware resources. This architecture is designed to separate resource protection from management to facilitate application-specific customization.
Let’s try to understand how this actually works.

The ultimate idea behind the development of exokernel is to impose as few abstractions as possible on the developers of the applications by providing them with the freedom to use the abstractions as and when needed. This ensures that there is no forced abstraction, which is what makes exokernel different from micro-kernels and monolithic kernels.But, how does exokernel support this?
This is done by moving all the hardware abstractions into untrusted user-space libraries called “library operating systems” (libOS), which are linked to applications call the operating system on their behalf. So basically, the kernel allocates the basic physical resources of the machine (disk blocks, memory, and processor time) to multiple application programs, and each program decides on what to do with these resources.
For an example, an application can manage its own disk-block cache, it can also share the pages with the other applications, but the exokernel allows cached pages to be shared securely across all applications. Thus, the exokernel protects pages and disk blocks, but applications manage them.
Of course, not all applications need customized resource management. At these instances, the applications can be linked with the support libraries that implement the abstractions that the applications need. However, library implementations are unprivileged and can therefore be modified or replaced at the user’s needs as well. This helps the programmers to choose what level of abstraction they want, high, or low.
Principles of Exokernels
1. Separate protection and management : Resource management is restricted to functions necessary for protection.
2. Expose allocation : Applications allocate resources explicitly.
3. Expose name : Exokernels use physical names wherever possible.
4. Expose revocation : Exokernels let applications to choose which instance of a resource to give up.
5. Expose information : Exokernels expose all system information and collect data that applications cannot easily derive locally.
Merits of Exokernels
- Significant performance increase.
- Applications can make more efficient and intelligent use of hardware resources by being aware of resource availability, revocation and allocation.
- Ease development and testing of new operating system ideas. (New scheduling techniques, memory management methods, etc)
Demrits of Exokernels
1. Complexity in design of exokernel interfaces.
2. Less consistency.


Comments
Post a Comment